Imagine you're trying to send a picture to a friend, but the system you're using can only handle text. How can you send the image? This is where Base64 encoding steps in! It’s like a translator that takes complex binary data (like images) and turns it into plain text that can be shared over text-based systems.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- Converting an image to Base64.
- Converting Base64 back to an image.
By the end, you'll have a solid understanding of how to use Base64 in JavaScript for your web development needs.
What is Base64 Encoding?
Base64 is a way of encoding binary data (like images, files, or special characters) into a string of ASCII text. This is important because raw binary data isn’t always compatible with systems that only understand text, like web pages or APIs. Base64 solves this problem by ensuring data is text-friendly while retaining the original information.
Think of Base64 as packing a gift into a box. The wrapping doesn’t change the gift itself, but it makes it easier to handle and deliver!
Why Use Base64?
Base64 encoding is widely used in web development for:
- Compatibility: It allows you to safely send binary data through text-based systems like HTML, JSON, or APIs.
- Embedding Images: You can embed images directly into web pages or emails, avoiding external file links.
- Simplified Data Transfers: When sending images or files via APIs, Base64 ensures the data is easy to handle as a string.
1. How to Convert an Image to Base64 in JavaScript
JavaScript provides built-in tools like the FileReader API to easily convert images to Base64 in the browser.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Select the Image File
Use an HTML <input> element to allow users to select an image.
<input type="file" id="fileInput" />
Step 2: Read the File with FileReader
The FileReader API reads the selected file in binary format and converts it to Base64.
Note: The FileReader API is a built-in JavaScript interface that helps in reading file contents asynchronously.
const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
fileInput.addEventListener('change', () => {
const file = fileInput.files[0];
const reader = new FileReader(); // FileReader reads file contents
reader.onload = () => {
const base64String = reader.result.split(',')[1]; // Extract Base64 string
console.log(base64String); // Output the Base64 string
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file); // Converts file to Base64 as Data URL
});
Step 3: Capture Base64 in a Textarea To make the Base64 string more accessible, display it in a textarea.
<textarea id="base64Output" rows="10" cols="50"></textarea>
Enhance the script to display the Base64 string:
const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
const base64Output = document.getElementById('base64Output');
fileInput.addEventListener('change', () => {
const file = fileInput.files[0];
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = () => {
const base64String = reader.result.split(',')[1];
base64Output.value = base64String; // Display the Base64 string in the textarea
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
});
Full Example for Converting Image to Base64
Here’s the complete HTML and JavaScript code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Convert Image to Base64</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Convert Image to Base64</h1>
<input type="file" id="fileInput" />
<textarea id="base64Output" rows="10" cols="50"></textarea>
<script>
const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
const base64Output = document.getElementById('base64Output');
fileInput.addEventListener('change', () => {
const file = fileInput.files[0];
const reader = new FileReader(); // Reads file content asynchronously
reader.onload = () => {
const base64String = reader.result.split(',')[1];
base64Output.value = base64String; // Display Base64 output
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file); // Reads file as Base64 Data URL
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
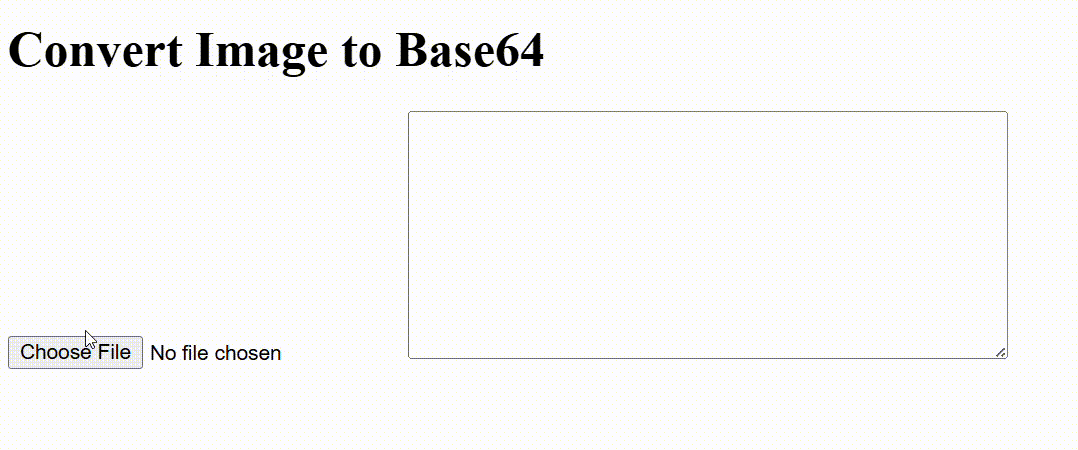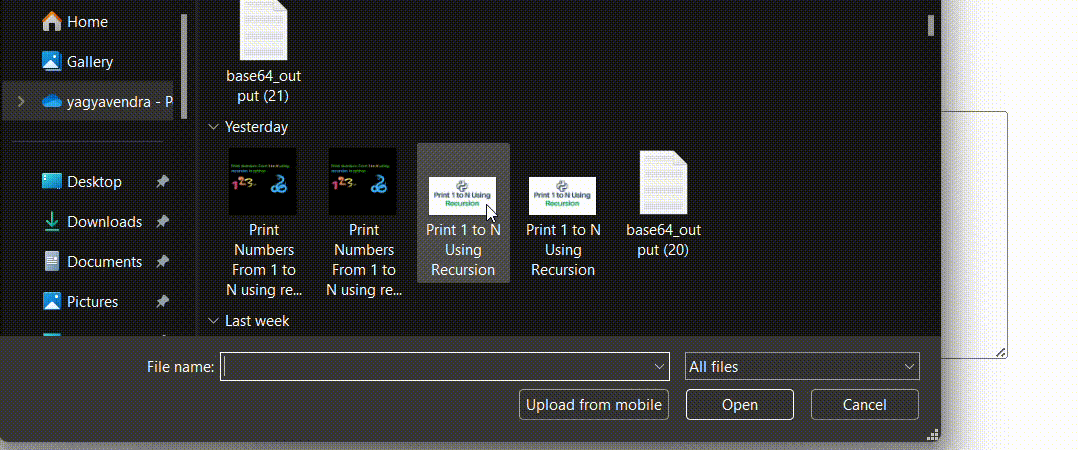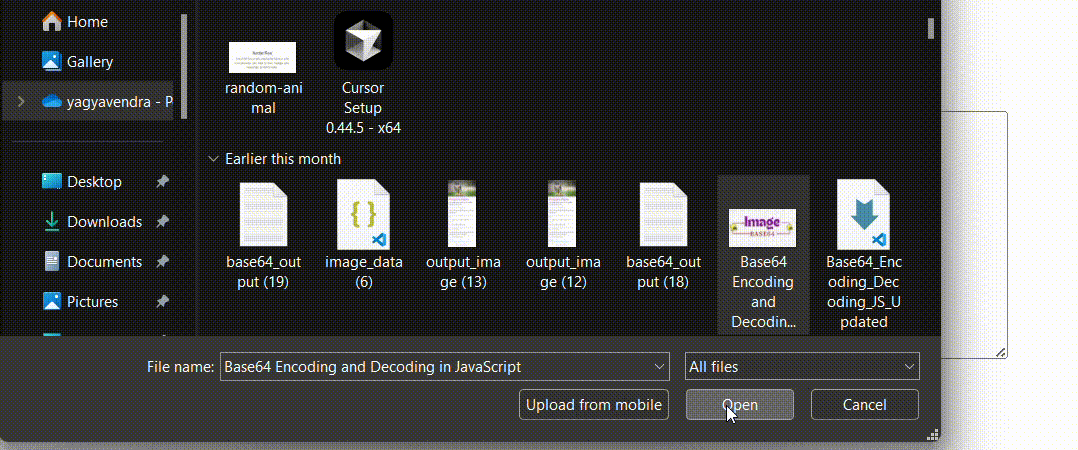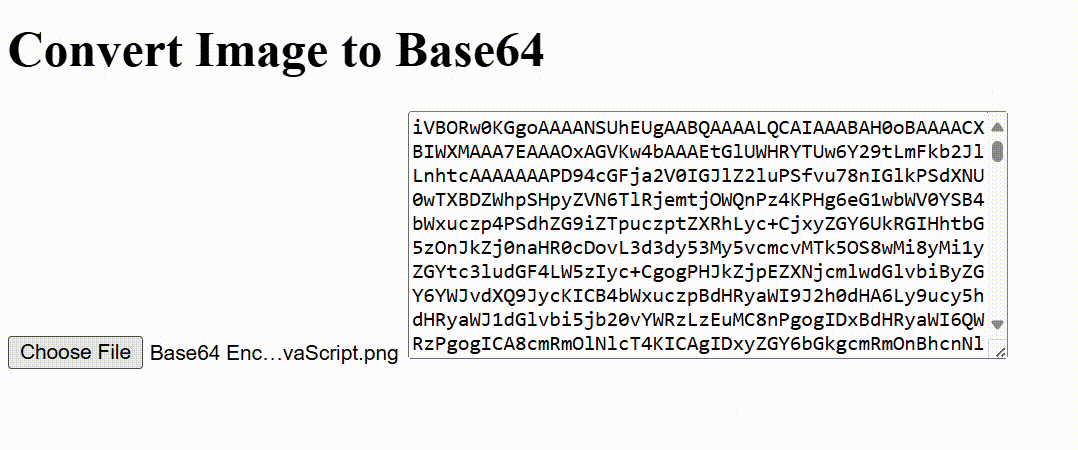
2. How to Convert Base64 Back to an Image in JavaScript
Converting a Base64 string back to an image is just as simple. JavaScript allows you to create a downloadable image file using a Blob object.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Base64 String Input Create a textarea for the Base64 string and a button to trigger the conversion.
<textarea id="base64Input" rows="10" cols="50">Paste your Base64 string here...</textarea>
<button id="convertButton">Download Image</button>
Step 2: Decode and Download the Image Use the following JavaScript to convert the Base64 string into a downloadable image:
Note: The atob function decodes a Base64 string back into binary data, while the Blob object lets you create binary data files in JavaScript.
const convertButton = document.getElementById('convertButton');
const base64Input = document.getElementById('base64Input');
convertButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
const base64String = base64Input.value; // Retrieve Base64 string
const binaryData = atob(base64String); // Decode Base64 to binary
const byteArray = new Uint8Array(binaryData.length); // Create binary array
for (let i = 0; i < binaryData.length; i++) {
byteArray[i] = binaryData.charCodeAt(i); // Convert binary to byte array
}
const blob = new Blob([byteArray], { type: 'image/png' }); // Blob stores binary data
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob); // Create downloadable URL
const link = document.createElement('a'); // Temporary link for download
link.href = url;
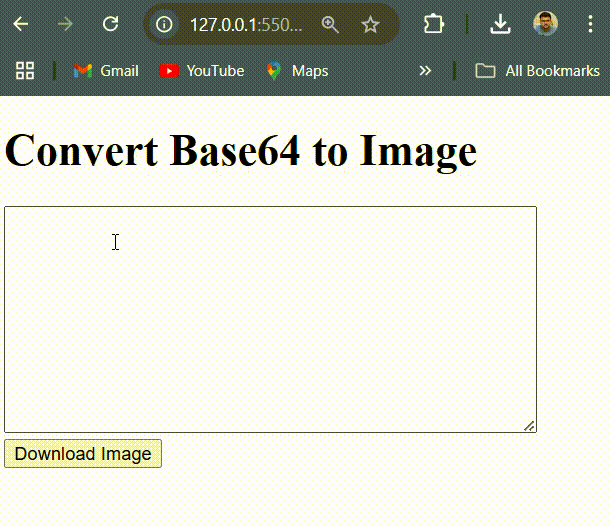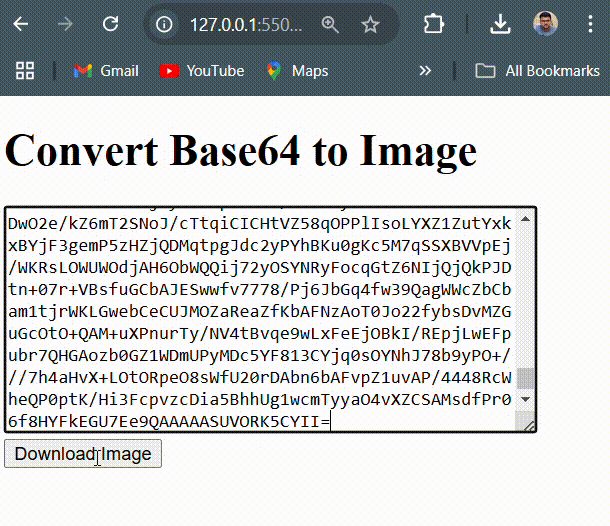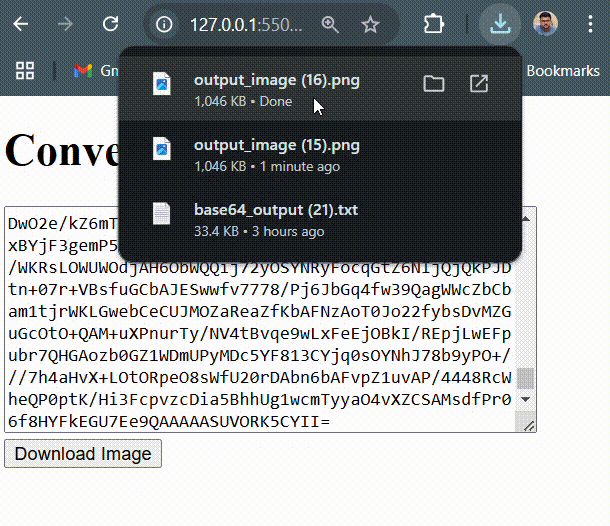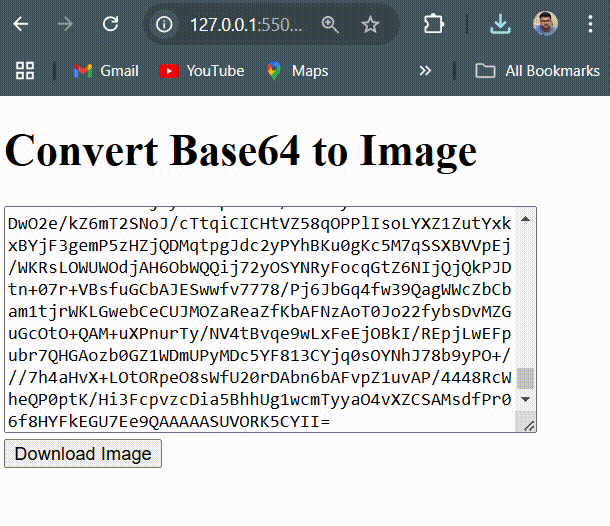
link.download = 'output_image.png'; // Set file name
link.click(); // Trigger download
});
Full Example for Converting Base64 to an Image
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Convert Base64 to Image</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Convert Base64 to Image</h1>
<textarea id="base64Input" rows="10" cols="50">Paste your Base64 string here...</textarea>
<button id="convertButton">Download Image</button>
<script>
const convertButton = document.getElementById('convertButton');
const base64Input = document.getElementById('base64Input');
convertButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
const base64String = base64Input.value;
const binaryData = atob(base64String); // Decode Base64 to binary
const byteArray = new Uint8Array(binaryData.length); // Convert binary to array
for (let i = 0; i < binaryData.length; i++) {
byteArray[i] = binaryData.charCodeAt(i);
}
const blob = new Blob([byteArray], { type: 'image/png' }); // Create Blob for binary
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob); // Generate object URL
const link = document.createElement('a');
link.href = url;
link.download = 'output_image.png';
link.click(); // Trigger download
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
Practical Applications of Base64 Encoding
- Embedding Images in HTML
Embed images directly into HTML documents using the
srcattribute:
<img src="data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABAAAAA..." />
Transmitting Images via APIs Send images over RESTful APIs by encoding them into Base64 strings.
Storing Images in Databases Store images as Base64 strings when direct binary storage isn’t feasible.
Conclusion
Base64 encoding and decoding are powerful tools for handling binary data in web development. With JavaScript, these processes are straightforward and efficient. Whether you’re embedding images in HTML, sending them through APIs, or converting them back into files, Base64 is an invaluable technique.
Try it out in your next project and see the difference it makes. Happy coding!


